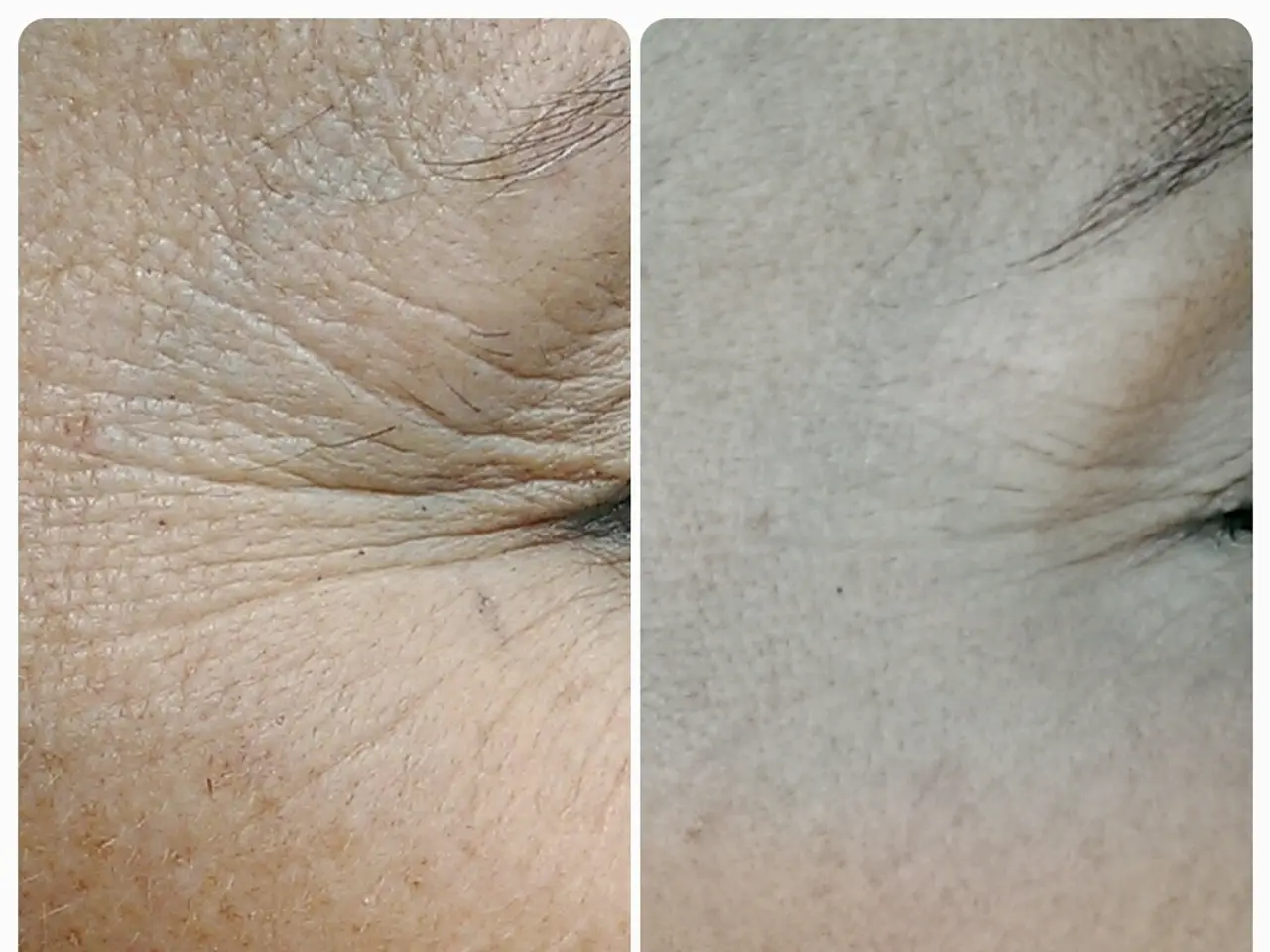
Skin, Hair, and Lip Hydration: Key Ingredients and their Advantages
In the world of skincare and haircare, understanding the role of humectants, emollients, and occlusives can make a significant difference. These three key ingredients have distinct functions that contribute to the hydration and protection of our skin and hair.
Humectants, such as hyaluronic acid, glycerin, aloe vera, and urea, work by attracting and drawing moisture into the skin, often from the deeper layers or even the environment. They are typically found in lightweight, water-based moisturizers and are ideal for hydrating dehydrated or oily skin by making it feel plumper and more supple.
Emollients, on the other hand, act primarily by softening and smoothing the skin’s surface and repairing the skin barrier. They fill gaps between skin cells with lipids, which helps to make rough, flaky skin feel more comfortable and supple. Emollients often include ingredients like cocoa butter, shea butter, squalene, and vegetable oils. They also provide a degree of moisture retention by forming a protective film, thus reducing water loss. Emollients are particularly useful for dry or eczema-prone skin and improve skin texture and softness.
Occlusives function as physical barriers on the skin surface that strongly prevent water loss by sealing in moisture. They tend to be thicker, oil- or wax-based ingredients such as petroleum jelly, beeswax, silicones, and petrolatum. Occlusives are best for severely dry skin conditions, like eczema, where water retention is critical, and they help prevent further moisture evaporation from the skin.
In hair care, humectants attract water to the hair shaft, helping keep it hydrated. This can be particularly beneficial for those with dry hair.
Consulting a dermatologist can help identify a person's skin type and find the best regimen for them. For those with oily skin, choosing products with "oil-free" and "noncomedogenic" on the label is advisable.
It's important to note that while these ingredients generally provide benefits, overuse or improper formulation can lead to skin irritation or follicle blockage.
In addition to their hydrating properties, some ingredients have other benefits. For example, urea helps enhance the stratum corneum by increasing hydration and improving the skin barrier's integrity. Hyaluronic acid promotes new blood vessel formation and increases fibroblasts, which produce collagen and other fibers. It can also speed up wound repair and reduce scar appearance.
Furthermore, a humectant-rich moisturizer containing 15% AHAs and 15% urea can remove scales, increase skin hydration, and reduce thickness of hyperkeratosis in people with thickened skin. Occlusives provide a layer on the skin surface that helps protect against water evaporation, preventing dry skin and eczema.
In conclusion, humectants hydrate by attracting water, emollients soften and improve skin barrier function while retaining some moisture, and occlusives protect the skin by preventing moisture loss through a barrier. Many moisturizers combine these agents for optimal hydration and skin care benefits.
Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) can help remove scales on the skin and increase hydration, making them beneficial for skin conditions like hyperkeratosis. A moisturizer containing 15% AHAs and 15% urea can provide these benefits.
Overuse or improper formulation of humectants, emollients, and occlusives can lead to skin irritation or follicle blockage, highlighting the importance of understanding these ingredients in health and wellness, skin care, and medical-conditions.
Urea plays a role in enhancing the stratum corneum, improving the skin barrier's integrity, and increasing hydration in the skin. It's found in some humectants like hyaluronic acid.
Hyaluronic acid, in addition to attracting moisture, promotes new blood vessel formation, increases fibroblasts, and speeds up wound repair, reducing scar appearance.
Dry skin conditions, such as eczema, can be managed with occlusives like petroleum jelly and beeswax, which function as physical barriers to prevent water loss and further moisture evaporation from the skin.